What Is Ionisation Energy For Class 8
There you can find the metals semi-conductors non-metals inert noble gasses Halogens Lanthanoides. The 1 ionization energy of magnesium is high but 2nd ionization energy is very high.
 What Is An Explanation For The Ionisation Energy Of D Block Elements Quora
What Is An Explanation For The Ionisation Energy Of D Block Elements Quora
8 Ionization energy when supplied to an atom results in an Anion and a proton.
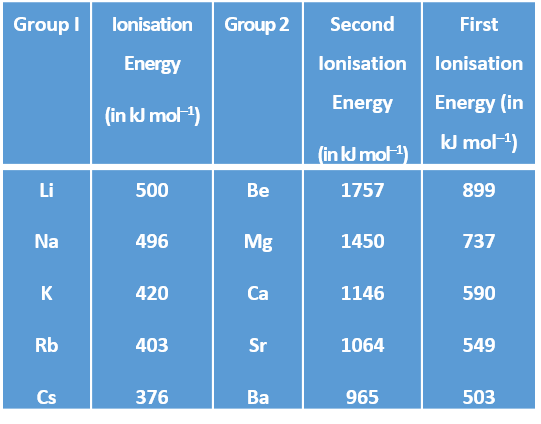
What is ionisation energy for class 8. The first or initial ionization energy or E i of an atom or molecule is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of isolated gaseous atoms or ions. The ionization energy associated with removal of the first most loosely held electron however is most commonly used. Moving left to right within a period or upward within a group the first ionization energy generally increases with exceptions such as aluminium and sulfur in the table above.
Cation and an Electron. Take a metal-alkali atom for example. 6 1 0 3 4 3 1 0 8 2 4 2 1 9.
The term ionization energy is a reference to the quantity or amount of energy necessary to expel an electron from the gaseous form of an atom or molecule. Anion and an electron. E 2181 1018 J.
The first ionisation energy is the energy involved in removing one mole of electrons from one mole of atoms in the gaseous state. It becomes very difficult to remove second electron from the Mg ion. 8 1 0 1 7 8.
This means that for 1 atom of hydrogen in the gaseous state you have. It is represented by i H. As electrons are removed it becomes more difficult to remove another because the charge of the atom has changed and the electron is more attracted to stay with the atom.
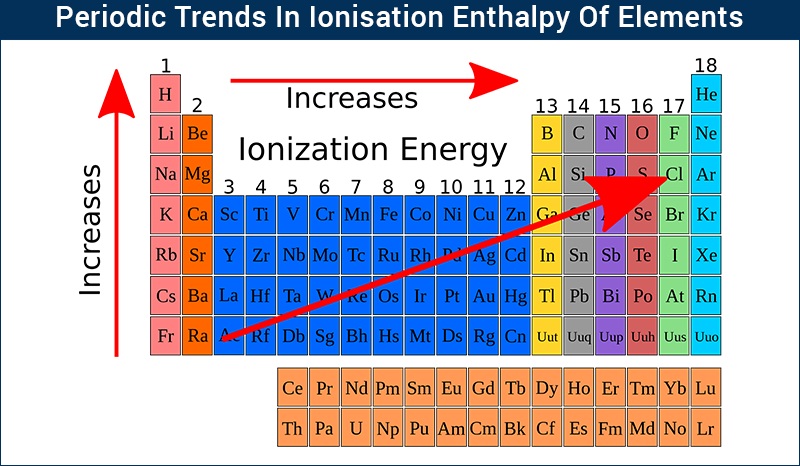
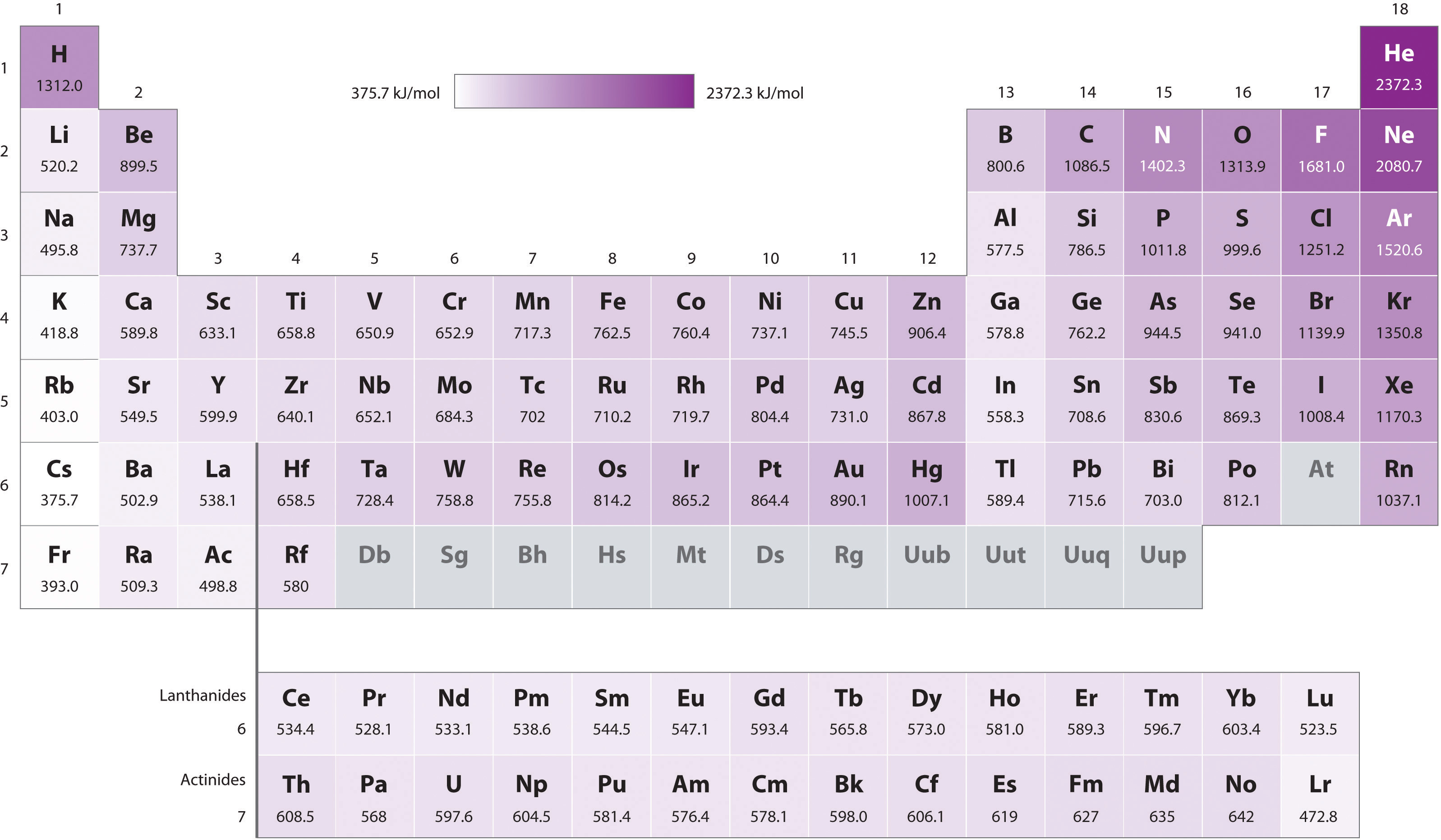
If sufficient energy is supplied electrons may be removed resulting in the formation of a positively charged ion. The ionisation energy for hydrogen atom is 136 eV. The ionization energy of an element increases as one moves across a period in the periodic table because the electrons are held tighter by the higher effective nuclear charge.
Its outer electron is in the second energy level much more distant from the nucleus. The energy required to remove the electron of the outermost valence from a neutral atom is the first energy of ionisation. The minimum energy required to remove an electron from an atom to infinitely far away is called the ionisation energy.
It is the amount of energy required to remove second electron from the ion. 1 8 1 0 1 5 J a t o m. Atom Energy cation.
The second frequency of ionisation is always higher than the energy of the first ionization. Ionization energy also called ionization potential in chemistry and physics the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an isolated atom or molecule. This means that in order to remove the electron from the ground state of a hydrogen atom in the gaseous state and create a hydrogen ion you need to supply 2181 1018 J of energy.
Ionisation energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom in its ground state to form a cation. The word required is used because it means ionization energy is positive that is it means it is always given from outside to remove electron. If we compare ionization energy.
The post is tagged and categorized under in 9th chemistry 9th notes. The ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from its orbital around an atom to a point where it is no longer associated with that atom. The element which has the highest ionization energy is Helium with 2458741 eV.
This is the post on the topic of the 9th class Chemistry Notes Chapter 8 - MCQsQuestions and Practicals pdf. This process may be represented as. 10 Gallium has a first ionization energy of 5788 kJmol and calcium has a first ionization energy of 5898 kJmol.
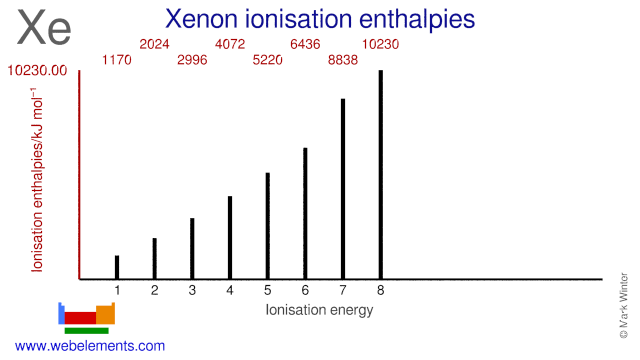
The second energy of ionization is that which is required to remove the next electron etc. An obvious feature of this graph is that the elements with the highest ionization energies are the noble gases. The minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from an isolated gaseous atom so to convert it into gaseous cation is called ionisation enthalpy.
There is an ionization energy for each successive electron removed. As the nuclear charge of the nucleus increases across the period the electron shielding remains constant hence the atomic radius decreases and. Ionization energy is also a periodic trend within the periodic table.
Ionization Energy E h v h v 66 10 34 3 10 8 242 10 9 198 242 10 17 818 10 15 J a t o m Ehvfrachvlambda frac66times 10-34times 3times 108242times 10-9frac198242times 1017818times 1015Jatom E h v h v 2 4 2 1 0 9 6. To list the elements order by ionization energy click on the table headers. Please note that the elements do not show their natural relation towards each other as in the Periodic system.
Cation and a proton. The unity for ionization energy is eV. You can print the list of elements by hitting the print button below.
It is otherwise called ionisation enthalpy. Above are the ionization energies of the elements are plotted against atomic number. Since the ionization energy measures the energy which must be supplied to remove an electron these high values mean that it is difficult to remove an electron from an atom of a noble gas.
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion. 9 Low first ionization energy is considered a property of. The value of the ionisation energy 2370 kJ mol-1 is much higher than hydrogen because the nucleus now has 2 protons attracting the electrons instead of 1.
It is close to the nucleus and unscreened. And the element which has the lowest ionization energy. Updated July 03 2019.
 Webelements Periodic Table Periodicity Ionization Energy 1st Periodic Table Gallery
Webelements Periodic Table Periodicity Ionization Energy 1st Periodic Table Gallery
 Webelements Periodic Table Periodicity Ionization Energy 9th Periodic Table Gallery
Webelements Periodic Table Periodicity Ionization Energy 9th Periodic Table Gallery
 Webelements Periodic Table Periodicity Ionization Energy 1st Periodic Table Gallery
Webelements Periodic Table Periodicity Ionization Energy 1st Periodic Table Gallery
 Ionization Energy Definition Trends Across Groups Periods With Videos
Ionization Energy Definition Trends Across Groups Periods With Videos
 7 4 Ionization Energy Chemistry Libretexts
7 4 Ionization Energy Chemistry Libretexts
 Periodic Trends Ionization Energy Explained With Exceptions Study Chemistry With Us Youtube
Periodic Trends Ionization Energy Explained With Exceptions Study Chemistry With Us Youtube
 Why Is The Ionization Energy Of Na Less Than Mg Quora
Why Is The Ionization Energy Of Na Less Than Mg Quora
 Identifying An Element From Successive Ionization Energies Worked Example Video Khan Academy
Identifying An Element From Successive Ionization Energies Worked Example Video Khan Academy
 Ionization Energy Or Ionisation Energy Of Group 1 Alkali Metals Elements Tuition Tube
Ionization Energy Or Ionisation Energy Of Group 1 Alkali Metals Elements Tuition Tube
 Ionization Energy Zirconium Zirconium Ppt Video Online Download
Ionization Energy Zirconium Zirconium Ppt Video Online Download
 Ionisation Energy Objectives To Define The Term Ionisation Energy To Describe And Explain The Trends In Ionisation Energy Across Period 3 And Down Group Ppt Download
Ionisation Energy Objectives To Define The Term Ionisation Energy To Describe And Explain The Trends In Ionisation Energy Across Period 3 And Down Group Ppt Download
 Webelements Periodic Table Xenon Properties Of Free Atoms
Webelements Periodic Table Xenon Properties Of Free Atoms
 Ionization Energy Trends Periodic Table Chemistry Khan Academy Youtube
Ionization Energy Trends Periodic Table Chemistry Khan Academy Youtube
 Variation Of Ionisation Energy Chemistry Knowledgeuniverseonline Com
Variation Of Ionisation Energy Chemistry Knowledgeuniverseonline Com
 The Ionization Energy Of The Ground State Of Hydrogen Atom Is 2 18 Xx 10 8 J Youtube
The Ionization Energy Of The Ground State Of Hydrogen Atom Is 2 18 Xx 10 8 J Youtube
Ionization Energy And Electron Affinity
 The Correct Order Of Ionisation Energy For Comparing Corbon Nitrogen And Youtube
The Correct Order Of Ionisation Energy For Comparing Corbon Nitrogen And Youtube
 Assertion The First Ionisation Energy Of Aluminium Is Lower Than That Of Magnesium Re Youtube
Assertion The First Ionisation Energy Of Aluminium Is Lower Than That Of Magnesium Re Youtube

Post a Comment for "What Is Ionisation Energy For Class 8"